2011年5月16日星期一
Periodic table trend
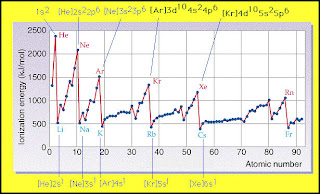
Ionization
-Ionization energy means the energy needed to remove electrons from an atom. Large atoms require low ionization energy while small atoms require high ionization energy. This quantity was formerly called ionization potential, and was at one stage measured in volts
Atomic Radius
-The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the size of its atoms, usually the mean or typical distance from the nucleus to the boundary of the surrounding cloud of electrons. Since the boundary is not a well-defined physical entity, there are various non-equivalent definitions of atomic radius.
Electro negativity:
-Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself and thus the tendency to form negative ions
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Periodic table history and Family of periodic table
Periodic table history
-A necessary prerequisite to the construction of
the periodic table was the discovery of the individual elements.
-By 1869, a total of 63 elements had been discovered.
--------------------------------------------
-Between 1863 and 1866 John Newlands
showed that by assigning Hydrogen an
arbitrary mass of 1 and ordering the known
elements by their masses, every eighth
element shared a common set of properties
-He called this the “law of octaves
----------------------------------------------
-1869, Dimitri Mendeleev published a method of
organizing the elements according to both
their masses and their properties.
-Mendeleev showed that when the elements
are listed according to masses, certain
properties recur PERIODICALLY.
- He broke the list into a series of rows
(PERIOD) and columns (GROUP).
-----------------------------------------------
l He placed elements in certain groups based on
their properties in spite of contrary indications by its
mass
Mendeleev left gaps in his table for elements, which
he proposed had yet to be discovered.
He was able to predict the properties and
characteristics of the undiscovered elements so
accurately that when they were discovered the
predicted value was quite exact.
The periodic table allowed chemists to organize
and understand their data and predict new
----------------MODERN PERIODIC TABLE-----------------------------
Is organized according to atomic number rather than
atomic mass. (This solved the problems where
different isotopic abundances caused the masses to
be “out of order”. Example: Ar and K, Co and Ni)
The periodic law summarizes the periodic table.
l The Periodic Law: Properties of the chemical elements
recur periodically when the elements are arranged from
lowest to highest atomic numbers
Major Divisions in the Periodic Table
l Period: The set of all elements in a given row going
across the table.
l Group or Family: The set of all elements in a given
column going down the table.
-------------------------------------------------------
THE Family of Periodic table
----Alkali Metal = elements in the first column (Except H)
----Alkaline Earth Metals = The elements in the second column
----Halogens = second column from the end on the right hand side. Starting with Fluorine.
----Noble Gases = Far right side of the table. Starting with helium.
----Lanthanide = elements in the first row shown underneath the table. Starting with lanthanum.
----Actinides = underneath the Lanthanides. Starting with actinium.
..................................................
Metals, Nonmetals, Semiconductors
Metal: reflect light when polished
are opaque
are good conductors of electricity and heat
are malleable or rolled into thin sheets and ductile
are usually solid at room temperatures
..........................................................
Non metals
Non metal: liquids or brittle solids at room temperature
Poor conductors of heat and electricity
Solids are dull to lustrous in appearance and opaque to translucent
Non – Metals can be divided into two subgroups:
1.Very low electrical conductivities
2.Fair to moderate conductivities
.........................................................
Semiconductor
A non-metal having an electrical conductivity, which increases with teperature.
Semiconductors (Metalloids or Semimetals) have properties which resemble metals more than nonmetals
Important difference is that metal conductivity
decreases with increasing temperature whereas the electrical conductivity of semiconductors
increases with increasing temperature.
0.................................................
-A necessary prerequisite to the construction of
the periodic table was the discovery of the individual elements.
-By 1869, a total of 63 elements had been discovered.
--------------------------------------------
-Between 1863 and 1866 John Newlands
showed that by assigning Hydrogen an
arbitrary mass of 1 and ordering the known
elements by their masses, every eighth
element shared a common set of properties
-He called this the “law of octaves
----------------------------------------------
-1869, Dimitri Mendeleev published a method of
organizing the elements according to both
their masses and their properties.
-Mendeleev showed that when the elements
are listed according to masses, certain
properties recur PERIODICALLY.
- He broke the list into a series of rows
(PERIOD) and columns (GROUP).
-----------------------------------------------
l He placed elements in certain groups based on
their properties in spite of contrary indications by its
mass
Mendeleev left gaps in his table for elements, which
he proposed had yet to be discovered.
He was able to predict the properties and
characteristics of the undiscovered elements so
accurately that when they were discovered the
predicted value was quite exact.
The periodic table allowed chemists to organize
and understand their data and predict new
----------------MODERN PERIODIC TABLE-----------------------------
Is organized according to atomic number rather than
atomic mass. (This solved the problems where
different isotopic abundances caused the masses to
be “out of order”. Example: Ar and K, Co and Ni)
The periodic law summarizes the periodic table.
l The Periodic Law: Properties of the chemical elements
recur periodically when the elements are arranged from
lowest to highest atomic numbers
Major Divisions in the Periodic Table
l Period: The set of all elements in a given row going
across the table.
l Group or Family: The set of all elements in a given
column going down the table.
-------------------------------------------------------
THE Family of Periodic table
----Alkali Metal = elements in the first column (Except H)
----Alkaline Earth Metals = The elements in the second column
----Halogens = second column from the end on the right hand side. Starting with Fluorine.
----Noble Gases = Far right side of the table. Starting with helium.
----Lanthanide = elements in the first row shown underneath the table. Starting with lanthanum.
----Actinides = underneath the Lanthanides. Starting with actinium.
..................................................
Metals, Nonmetals, Semiconductors
Metal: reflect light when polished
are opaque
are good conductors of electricity and heat
are malleable or rolled into thin sheets and ductile
are usually solid at room temperatures
..........................................................
Non metals
Non metal: liquids or brittle solids at room temperature
Poor conductors of heat and electricity
Solids are dull to lustrous in appearance and opaque to translucent
Non – Metals can be divided into two subgroups:
1.Very low electrical conductivities
2.Fair to moderate conductivities
.........................................................
Semiconductor
A non-metal having an electrical conductivity, which increases with teperature.
Semiconductors (Metalloids or Semimetals) have properties which resemble metals more than nonmetals
Important difference is that metal conductivity
decreases with increasing temperature whereas the electrical conductivity of semiconductors
increases with increasing temperature.
0.................................................
2011年5月15日星期日
The Electron configuration
-Energy Level is a specific amount of energy which an electron in an atom can possess
- n is the # of energy level
-the energy different between 2 particular energy level is called quantum of energy
-Orbit is the actual region of space occupied by an electron in a particular energy level
- n=1:only the s-type is possible
- n=2:the s and p types are possible
- n=3:the s p and d types are possible
- n=4: the s p d f types are possible
-----------------------------------
- s type sub shell consists of 1 s-orbital
- p type sub shell consists of 3 p-orbital
- d type sub shell consists of 5 d-orbital
- f type sub shell consists of 7 f-orbital
-2 Electron can be placed in each orbit
-a shell is the set of all orbitals having the same N- value
E.g the third shell consists of the 3s 3p 3d orbitals
-a subshell is a set of orbitals of the same type
- An electron configuration is a description of which orbitals in an stom electron configuration
E.g Ne(1s2 2s2 2p6)
=---------------------------------------------
Core Notation
-the set of electrons belonging to a given atom can be divided into 2 subsets: the core electrons and th outer electrons
-CORE: the set of electrons with the configuration of the nearest noble gas having an atomic number Less than that of the atom being considered
E.g Al(1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1)------>Al([Ne] 3s2 3p1 )
CORE OUTER
EXCEPTION:
Cr([Ar]4s2 3d4)---->Cr([Ar]4s1 3d5) --to make 2 half filled sub shells
Cu([Ar]4s2 3d9)---->Cr([Ar]4s1 3d10)--to make a hall filled sub shell and a filled sub shell
-----------------------------------------------------
- n is the # of energy level
-the energy different between 2 particular energy level is called quantum of energy
-Orbit is the actual region of space occupied by an electron in a particular energy level
- n=1:only the s-type is possible
- n=2:the s and p types are possible
- n=3:the s p and d types are possible
- n=4: the s p d f types are possible
-----------------------------------
- s type sub shell consists of 1 s-orbital
- p type sub shell consists of 3 p-orbital
- d type sub shell consists of 5 d-orbital
- f type sub shell consists of 7 f-orbital
-2 Electron can be placed in each orbit
-a shell is the set of all orbitals having the same N- value
E.g the third shell consists of the 3s 3p 3d orbitals
-a subshell is a set of orbitals of the same type
- An electron configuration is a description of which orbitals in an stom electron configuration
E.g Ne(1s2 2s2 2p6)
=---------------------------------------------
Core Notation
-the set of electrons belonging to a given atom can be divided into 2 subsets: the core electrons and th outer electrons
-CORE: the set of electrons with the configuration of the nearest noble gas having an atomic number Less than that of the atom being considered
E.g Al(1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1)------>Al([Ne] 3s2 3p1 )
CORE OUTER
EXCEPTION:
Cr([Ar]4s2 3d4)---->Cr([Ar]4s1 3d5) --to make 2 half filled sub shells
Cu([Ar]4s2 3d9)---->Cr([Ar]4s1 3d10)--to make a hall filled sub shell and a filled sub shell
-----------------------------------------------------
Atomic structure
-the chemical elements are different from the other by the # of proton
E.g- N:7 proton in the nucleus
- O:8 proton in the nucleus
- Cl: 17 proton in the nucleus
-Atomic Number: the number of protons in the nucleus
---A neutral atom has no charge, # of electrons = # of protons
E.g: The atomic number of Cl is 17
-any atom of Cl has 17 protons
-a neutral Cl has 17 electrons
-electrons are gained or lost roam neutral atom is called Ion
---------------------------------------------
Atomic Mass is the total number of protons ans neutrons
∴ #of protons + #of neutrons = Atomic Mass
E.g Carbon 12/6 C
#of protons = atomic number = 6
#of electrons = 6
#of neutrons = 12-6=6
------------------------------------------------
Isotopes are atomic species having the same atomic number but different atomic masses
E.g 19/9 F + 1/0n ----20/9 F
-----------------------------------------
E.g- N:7 proton in the nucleus
- O:8 proton in the nucleus
- Cl: 17 proton in the nucleus
-Atomic Number: the number of protons in the nucleus
---A neutral atom has no charge, # of electrons = # of protons
E.g: The atomic number of Cl is 17
-any atom of Cl has 17 protons
-a neutral Cl has 17 electrons
-electrons are gained or lost roam neutral atom is called Ion
---------------------------------------------
Atomic Mass is the total number of protons ans neutrons
∴ #of protons + #of neutrons = Atomic Mass
E.g Carbon 12/6 C
#of protons = atomic number = 6
#of electrons = 6
#of neutrons = 12-6=6
------------------------------------------------
Isotopes are atomic species having the same atomic number but different atomic masses
E.g 19/9 F + 1/0n ----20/9 F
-----------------------------------------
订阅:
博文 (Atom)